The Power Of Ontologies
In the Axone protocol, ontologies are indispensable. They facilitate a comprehensive depiction of the dataverse, capturing even its most intricate details. Ontologies provide detailed descriptions of both datasets and services, enhancing overall comprehension. Moreover, they bridge the connection between governance and orchestration within the dataverse.
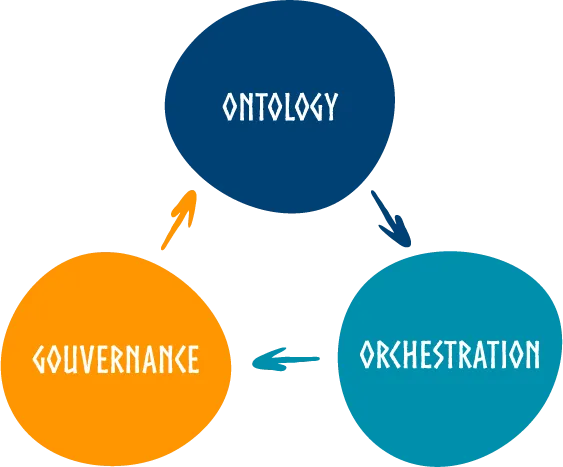
This ontology allows to achieve:
- Standardization of terminology: standardized terminology is used for concepts and relationships in a given domain, clarifying and avoiding misunderstandings between participants.
- Structuring of data: data is structured in a coherent and organized way, making it easier to access, process, and analyze.
- Interoperability of systems and tools: a well-designed ontology enables interoperability between systems and tools, facilitating the sharing of knowledge among different stakeholders.
- Improved data research and analysis by accurately describing concepts and relationships in a particular domain.
A formal model for the Axone protocol
This ontology describes and defines the different forms of vocabularies used in the Axone protocol in a standard and well designed format. The aim is to model a semantic network of all the entities (Zones, data, services, processing workflows) by semantically characterizing what they are and the relationships they maintain between them. Thus, the ontology provides a complete living understanding and knowledge of the datasets within a Zone, their transformation (by the services), as well as the governance rules that apply (data sharing, consents, policy rules).
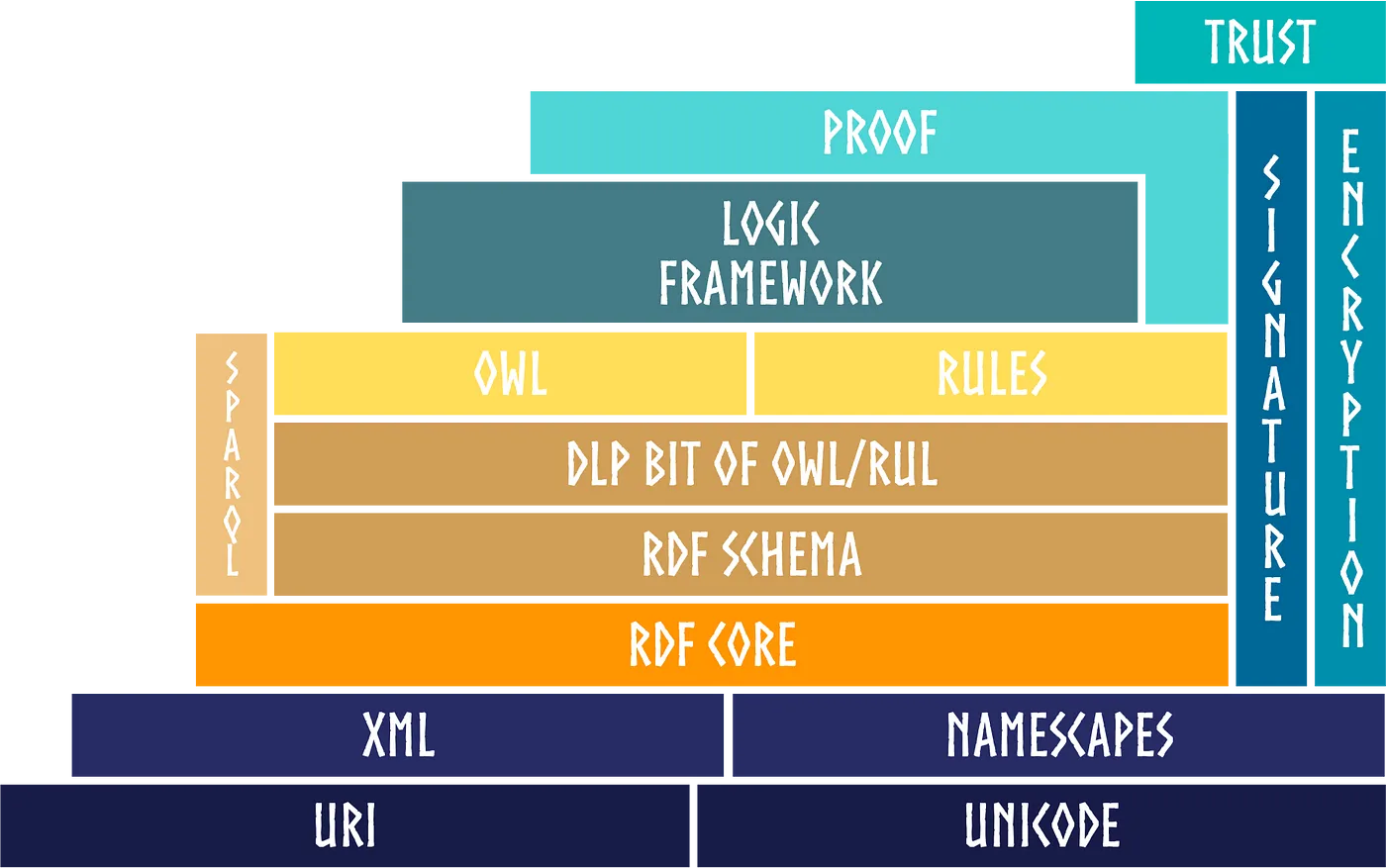
Several languages are used to express the Axone ontologies:
- OWL (Web Ontology Language): a standard language of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) for representing ontologies. OWL is based on descriptive logic and allows for the definition of classes, subclasses, properties, and relationships.
- RDF (Resource Description Framework): a markup language for representing information about resources on the Web, including ontologies. RDF describes resources in terms of their properties and relationships with other resources.
- RDFS (RDF Schema): an ontology representation language that defines classes and properties and relationships between them. RDFS is an extension of RDF.
- SKOS (Simple Knowledge Organization System): a language for representing ontology that allows the description of classification systems and thesauri. SKOS allows the definition of concepts, relationships, and properties.
Ontology at the heart of the blockchain
The Ontology is at the heart of the Axone protocol as much of the information is encoded and stored as an ontology on-chain in the blockchain transactions. This means that (almost) all the semantics of the transactions submitted to the blockchain are expressed through this ontology - for instance the creation of a Zone, the execution of a Service, the description of a Dataset, etc.